6.4.4 Explain the Structure of Domain System
Single Domain
Updated: March 28, 2003Applies To: Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2003 R2, Windows Server 2003 with SP1, Windows Server 2003 with SP2
A single domain model is the easiest to administer and the least expensive to maintain. It consists of a forest that contains a single domain. This domain is the forest root domain and it contains all of the user and group accounts in the forest.
A single domain forest model reduces administrative complexity by providing the following advantages:
Any domain controller can authenticate any user in the forest.
All domain controllers can be global catalogs; therefore, you do not need to plan for global catalog server placement.
In a single domain forest, all directory data is replicated to all geographic locations that host domain controllers. While this model is the easiest to manage, it also creates the most replication traffic of the two domain models. Partitioning the directory into multiple domains limits the replication of objects to specific geographic regions but results in more administrative overhead
Forest Domain :
At its highest level, a forest is a single instance of Active Directory. Therefore, a forest is synonymous with Active Directory, meaning that the set of all directory partitions in a particular Active Directory instance (which includes all domain, configuration, schema and optional application information) makes up a forest. This means that when you have multiple forests in an enterprise they will, by default, act separately from each other as if they were the only directory service in your organization.
This behavior, however, is easily be modified so that multiple forests can share Active Directory responsibilities across an enterprise. This is done by creating external or forest trust relationships between the forests. In this way, each forest can be connected with every other forest to form a collaborative directory service solution for any enterprise with business needs that include multiple forest collaboration.
Forests can also be defined as:
Collections of Domain Containers that Trust Each Other
Units of Replication
Security Boundaries
Units of Delegation
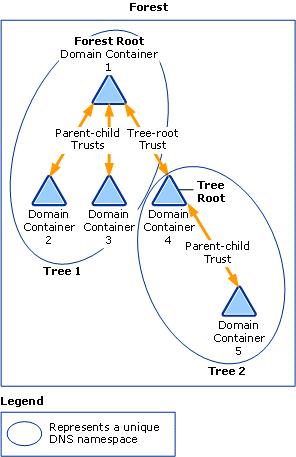
Forests can be used to segregate domain containers into one or more unique DNS namespace hierarchies known as domain trees


Comments
Post a Comment