Question
Definition
1.
What is operating system
installation?
Answer
Installation (or setup) of a program (including drivers, plugins) is
the act of putting the program onto a computer system so that it can be
executed.
Types of Operating System
Installation
2.
Explain these types of operating
system installation methods:
a.
Typical installation
b.
Full Installation
c.
Custom installation
d.
Minimal Installation
Answer
a. Typical
installation
·
The most installation common options and is
recommended for most users
·
The program will be installed with the
components and features that the manufacturer has chosen.
b. Full
Installation
·
The installer will ask whether you want to do a
full, minimal or custom installation.
·
“Full installation” is the default and will
install all sets.
·
Full install is removing what user already have and
doing a complete install.
·
A full installation is performed for new
installations to install the software from the CD to the hard drive.
c.
Minimal Installation
·
This minimal installation will install only the
base component. Some feature will install depend on manufacture has chosen.
·
Recommended for beginner user with low
performance or low hard disk space.
·
It is fast and simple installation.
d. Custom
installation
·
Give user complete control over which packages
user wish to install and the installation path that is used.
·
User needs to know exactly with features the may
need to choose.
Importance of Operating System maintenance
3.
Why the operating system needs to
be maintained?
Answer
a.
Maintenance is a step taken on a computer system
to reduce or prevent computers from experiencing minor or serious technical
problems.
b.
Save on the cost of purchasing or repairing
damaged hardware.
c.
Reduces or avoids minor damage.
d.
Extend the life of the computer.
e.
Extend the hardware life of a computer
accessory.
Operating System Maintenance
4.
Describe three process of
operating system maintenance.
Answer
Disk Cleanup
a. Allows users to
remove files that are no longer needed or that can be safely deleted.
b. Removing
unnecessary files, including temporary files, can help to speed up and improve
the performance of the hard drive and computer.
c. Running Disk
Cleanup at least once a month is an excellent maintenance task and frequency.
Disk Defragmenter
a.
Defragmenter is a Microsoft utility first included
with MS-DOS 6.0, and in all versions of Windows.
b.
It is designed to help chronologically order the data
on the hard drive.
c.
Defrag places each part of a program together instead
of scattered throughout the hard drive, allowing the read-write head to access
the data faster on the hard drive.
Delete Temporary Files
a. Having lots of
old temporary files stored by your computer long ago can slow down the machine.
b. User can delete
these manually, but a better option is to use software like CCleaner.
c. CCleaner
automatically clears temporary internet files for all installed browsers,
system temporary files, and even temp files for some other applications.
Pre-Installation Checklist
5.
Identify pre-installation
checklist for successful operating system installation.
Answer
STEP1
Verify all hardware is certified to
work with the selected OS.
STEP2
Verify that the hardware resources meet or exceed
published minimum requirements.
STEP3
Confirm the appropriate installation medium is
available. Due to the file size of current operating system, usually available
on both CD and DVD media
STEP4
If the OS is to be installed on a
system that already consist data:
a.
Use system diagnostic tools and utilities to
ensure that the current OS installation is in good condition, free of malicious
or damaging files and codes
b.
Complete a full backup of all important files
STEP5
If performing a clean install, verify that all
application software is available for installation
STEP 6
If connecting the computer to a network at this time,
verify that the network configuration is available
STEP7
If a different OS is to be installed, verify that the
use has adequate training in the new OS
STEP8
Before starting installation, determining the partition
structure. Depicts hard disk partitioning
Basic Option for Installation
6.
A customer asked you to repair a
computer system package with a corrupted operating system installed. As a
technical expert;
a.
List four basic options that are available for
the installation of a new operating system to the computer.
b.
Explain the options listed in question (a)
above.
Answer
a.
A clean install
i. Install
on a new system or in case where no upgrade path exists between the current OS
and the one being installed.
ii. It
deletes all data on the partition where the OS is installed and requires application
software to be installed.
iii. A
new computer system requires a clean install
iv. It
can be performed when the existing OS installation has become damaged in some
way.
b.
Upgrade
i. Refer
to the replacement of a product with a new version of that same product.
ii. If
user is staying with the same OS platform, doing an upgrade is often possible.
iii. With
an upgrade, system configuration settings, applications and data are preserved.
iv. It
simply replaces the old OS files with the new OS files.
c.
Multi-boot
i. Installing
more than one OS on a computer to create a multi-boot system is possible.
ii. Each
OS is contained within its own partition and can have its own files and
configuration settings.
iii. On
start-up, the user is presented with a menu to select the desired OS.
iv. Only
one OS can run at a time and it has full control of the hardware.
v. As
an example of multi-boot, it is possible to install Windows XP, Windows Server
and Linux on the same system.
vi. This
setup can be useful in a test environment where only one PC is available but
there is a need to test several different OS and applications.
d.
Virtualization
i. A
technique that is often deployed on servers.
ii. It
enables multiple copies of an OS to be run on a single set of hardware, thus
creating many virtual machines.
iii. Each
virtual machine can be treated as a separate computer.
iv. This
enables a single physical resource to appear to function as multiple logical
resources.
v. This
types of approach generally demands more physical resources such as CPU
processing and RAM because multiple OS’s are running on the same machine.
Patches for Operating System and Application Software
7.
Discuss patches for operating
system and application software in personal computer.
Answer
a.
Patches
will keep our computer protected from the viruses, spyware, adware, Trojan horses,
malware and hackers’ attacks and other online threats.
b.
To
protect the Windows computers, Microsoft intermittently releases the
latest patches and security updates to deal with the latest online threats. User
can configure the Windows based operating system to automatically update
itself.
c.
Operating
system contains the vulnerabilities and security lapses and that can be fixed
by installing the latest services packs, hot fixes and the security patches.
d.
Operating
system patches are the latest security updates that are released by the operating
system vendor such as Microsoft, Apple and Sun etc.
Apply Patches to Operating Systems
8.
Patches to operating systems can
be installed in different ways depending on the OS and the needs of the user.
Explain three options for downloading and installing updates include the
following:
a.
Automatic installation
b.
Prompt for permission
c.
Manual
Answer
Automatic installation
a.
The OS can be configured to connect to the
manufacturer’s website and then download and install minor updates without any
user intervention.
b.
Updates can be scheduled to occur during times
when the computer is on, but not in use.
Prompt for permission
a.
Some users want to have control over which
patches are applied.
b.
This choice is often the one for users who understand
what impact a patch can have on system performance.
c.
The system can be configured to notify the end
user when a patch is available.
d.
The user must then decide whether to download
and install the patch
Manual
a.
Updates that require major pieces of code to be
replaced on a system should be run manually.
b.
These major updates are often called service
packs and are designed to correct problems with an application or OS, and
sometimes to add functionality.
c.
These service packs usually require the end user
to manually connect to a website, download files, and install the update.
d.
They can also be installed from a CD available
from the manufacturer.
NTFS
9.
Define and describe NTFS
Answer
NTFS is New Technology File System
a.
There is built in security
b.
Data can be recovered
c.
File compression is one amongst several other
features.
d.
Maximum volume size is 2TB. Nearly unlimited
files can be stored.
FAT
10.
Define and Describe FAT
Answer
FAT is File
Allocation Table
a.
FAT is a computer file system architecture now
widely used on most computer systems and most memory cards, such as those used
with digital cameras.
b.
It was developed by Bill Gates and Marc McDonald
during 1976–1977.
c.
It is the primary file system for various
operating systems including DR-DOS, FreeDOS, MS-DOS, OS/2 (v1.1) and Microsoft
Windows (up until Windows Me).
d.
The FAT file system is relatively
straightforward technically and is supported by virtually all existing
operating systems for personal computers.
Product Keys
11.
Explain the product keys.
Answer
a.
Also known as a Software key,
b.
It is a specific software-based key for a
computer program.
c.
It certifies that the copy of the program is
original.
d.
Activation is sometimes done offline by entering
the key, or with software like Windows 7, online activation is required to
prevent multiple people using the same key.
e.
Not all software has a product key, as some
publishers may choose to use a different method to protect their copyright, or
in some cases, such as open source software, copyright protection is not used.
Structure of Domain System
12.
Explain the structure of domain
system.
Answer
a. Single
or multiple domain system
•
A single domain is the easiest to administer
•
Least expensive to maintain.
•
It consists of a forest that contains a single
domain. A single domain forest model reduces administrative complexity by
providing the following advantages:
•
All domain controllers can be global catalogues.
•
All directory data is replicated to all
geographic locations that host domain controllers.
•
The easiest to manage.
•
Creates the most replication traffic of the two
domain models.
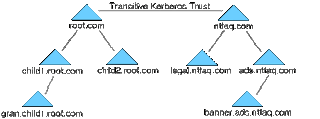
b. For (I.A.Dhotre, 2009) (Mohan, 2013) (Harris, 2001) est of domain
·
A collection of trees that don’t necessarily
form a contiguous namespace (although each tree must be contiguous).
·
This arrangement might be useful if a company has multiple root DNS addresses, as in the Figure.
This arrangement might be useful if a company has multiple root DNS addresses, as in the Figure.
Comments
Post a Comment